Electric Boiler: What Homeowners Need to Know
Table of Contents
This article provides a comprehensive overview of electric boilers, highlighting their functionality, types, advantages, and considerations for homeowners. Here’s a summarized breakdown of what homeowners need to know about electric boilers
Overview of Electric Boilers
Electric boilers are heating systems that use electricity to heat water, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gas boilers. They convert electrical energy into heat energy, providing instant hot water and heating for homes. Electric boilers can be connected to various systems, such as domestic water tanks, radiators, and underfloor heating.
How Electric Boilers Work
When activated, the heating element within the electric boiler heats the water. The heated water is then circulated via a pump through pipes to different heating systems or directly to a hot water tap.

Who Needs Electric Boilers?
Electric boilers are ideal for:
Homes without gas supply: Suitable for remote areas or specific buildings without access to gas.
Environmentally conscious homeowners: Reduce carbon footprint as they don’t use gas.
Extremely cold areas: Can be paired with other systems like heat pumps to enhance efficiency and warmth.
Homes with limited space: Compact design fits well in small apartments or older homes where space is limited.
Commercial and industrial applications: Suitable for offices and stores due to their clean, quiet, and efficient operation.
Types of Electric Boilers
Open-Vented Boilers
Requires external components like a circulation pump and expansion tanks.
Suitable for homes with space for external tanks, providing central heating and hot water.
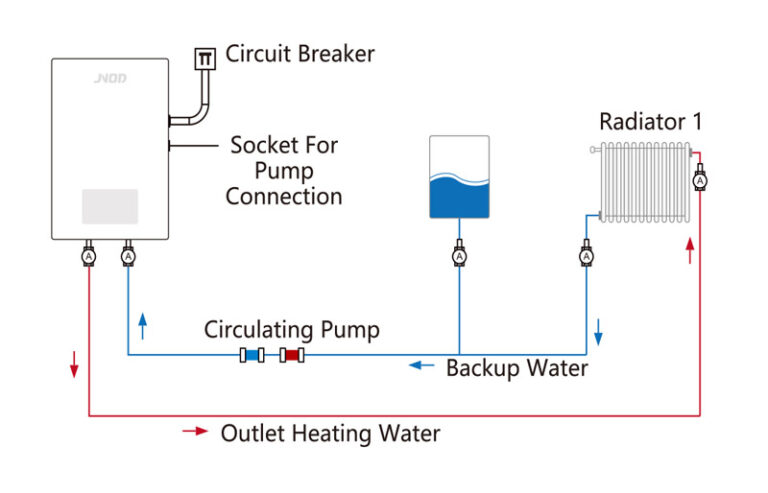
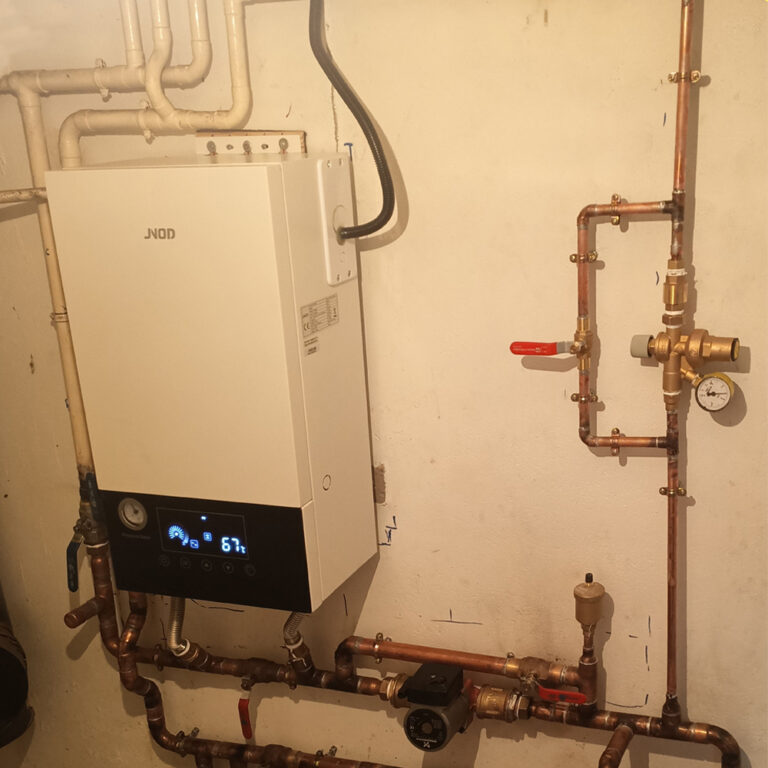
Electric System Boilers
Includes a built-in circulation pump and expansion vessel.
Single heating system, and needs to be connected to a water tank for storing hot water. It’s ideal for underfloor heating or multiple radiator setups.
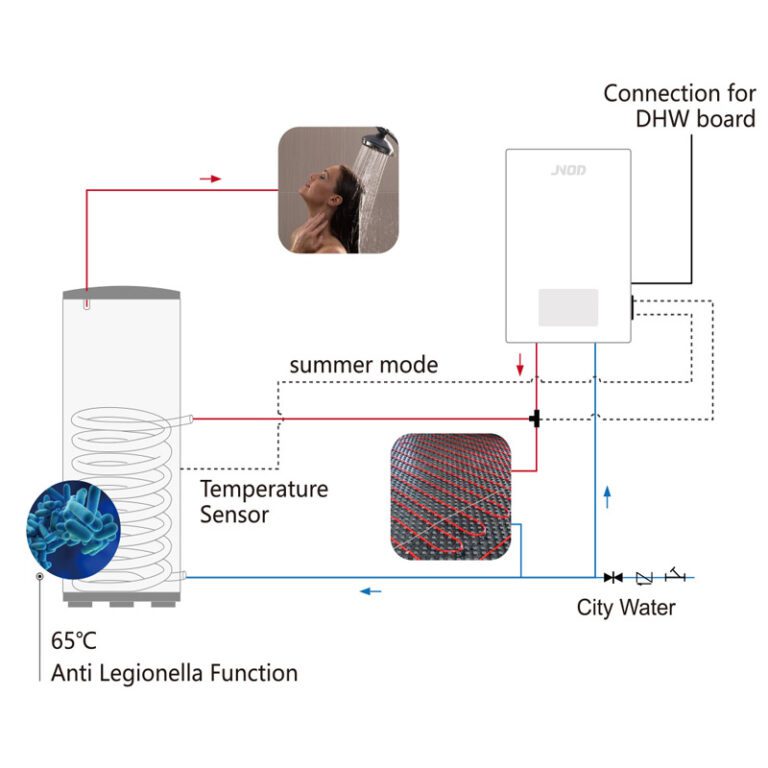
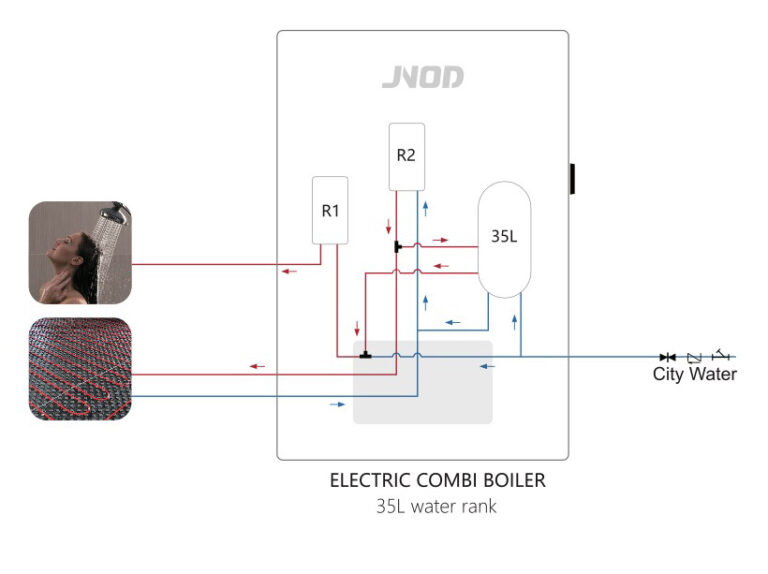
Electric Combi Boilers
This type also included a circulation pump and expansion vessel.
Features two heaters (one for heating, one for domestic hot water) and can include an internal water tank.
Best for smaller properties, offering on-demand heating and hot water without external tanks.
Advantages of Electric Boilers
Energy Efficiency: Nearly 100% efficient, converting almost all electrical energy into heat.
Ease of Installation: Simple to install, no flue or fuel storage needed.
Safety: No risk of gas leaks or carbon monoxide poisoning.
Environmental Impact: Eco-friendly when powered by renewable energy sources.
Low Maintenance Costs: Requires minimal servicing.
Space-Saving and Quiet Operation: Compact and operates with low noise levels.
Disadvantages of Electric Boilers
Higher Operating Costs: Electricity is generally more expensive than gas or oil.
Power Dependency: Completely reliant on electricity, which can be an issue during power outages.
Heating Capacity Limitations: May not be suitable for very large homes or buildings.
Sizing Your Electric Boiler
The size of the boiler depends on factors like property size, radiator count, hot water demand, insulation, and climate. Small homes might need a 6-9 kW boiler, while larger homes could require up to 24 kW. Consulting a professional for a heat load calculation is recommended for accurate sizing.
Conclusion
Electric boilers are a highly efficient, eco-friendly, and safe heating solution for homeowners, particularly when space is limited or gas is unavailable. JNOD offers a range of electric boilers that provide superior performance, energy efficiency, and reliability, making them a top choice for modern heating needs.

