Electric Boiler Internal Structure Guide for Installers and Contractors
Electric boilers are becoming an increasingly popular solution for heating systems, especially in regions moving away from gas. For installers and contractors, understanding the internal structure of an electric boiler is essential for proper installation, servicing, and ensuring long-term performance.
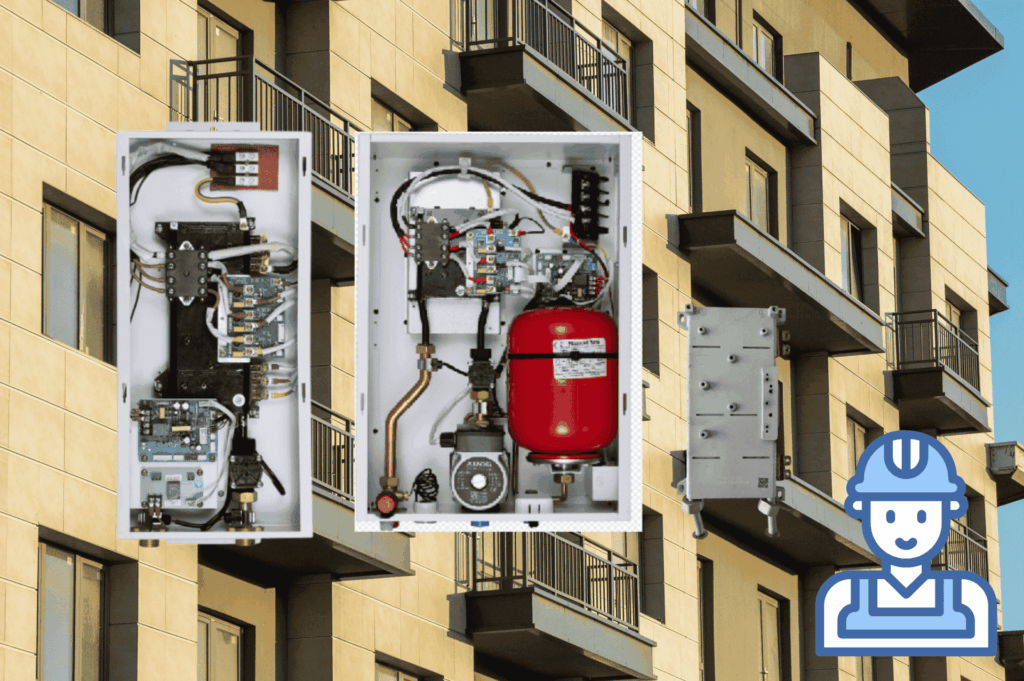
Key Internal Components of an Electric Boiler
Heating Elements
The core component of an electric boiler is the heating element. These resistive elements convert electricity into heat, which is transferred directly into the water.
- Typically made of stainless steel or cast aluminum for durability.
- Designed for high efficiency, often achieving 98–99% energy conversion.
JNOD electric boilers use patented heating elements that offer up to 99% heating efficiency and are scale-resistant. You can read more about these advantages in this article—— Innovative Heating Elements: How They Drive Energy Efficiency
Heat Exchanger
Some models use an integrated heat exchanger to improve thermal transfer and protect the heating elements from scaling. This ensures consistent water temperature and longer component lifespan.
Internal Water Tank (Optional)
Some models of combination or storage electric boilers come with a built-in domestic water tank, usually with a capacity of 30-50 litres. The JNOD BP-E electric combi boiler has a built-in 30L domestic water tank.
- Acts as a buffer to provide instant hot water.
- Eliminates the need for a large external cylinder, saving space and installation time.
Circulation Pump
Most modern electric boilers include a built-in circulation pump to distribute heated water throughout radiators, underfloor heating, or hydronic systems. This reduces the need for additional components during installation.
Expansion Vessel & Safety Components
To maintain system safety, electric boilers integrate:
- Expansion vessel – absorbs pressure changes as water heats.
- Safety relief valve – prevents dangerous overpressure.
- Pressure gauge – allows easy monitoring.
- Low-Water Cutout – A safety device that shuts off the heating element if the water level gets too low, preventing damage.
- Automatic Air Vent – An external component to release air from the system and prevent it from interfering with operation.
Control Panel & Electronics
The control system is the “brain” of the boiler, managing temperature, power modulation, and system diagnostics.
- Smart thermostats & Wi-Fi connectivity are increasingly integrated.
- Self-diagnosis systems help technicians quickly identify faults during service.
Why Installers Should Know the Internal Structure
- Simpler Installation: Many electric boilers arrive pre-assembled with pumps, expansion vessels, and controls already integrated. This reduces on-site work and installation errors.
- Easier Servicing: Understanding the internal structure helps contractors quickly identify components, troubleshoot issues, and replace faulty parts.
- Improved Customer Guidance: Being able to explain how the boiler works internally builds trust with clients and helps highlight efficiency, safety, and reliability benefits.
- Space-Saving Solutions: Knowing which models include built-in tanks or pumps allows you to recommend boilers that save space in small apartments or retrofit projects.
Conclusion
For installers and contractors, mastering the internal structure of electric boilers means faster installations, fewer callbacks, and greater customer satisfaction. From heating elements to smart control panels, every component contributes to performance, safety, and efficiency.
As demand for electric boilers grows in Europe and beyond, professionals who understand their design will be better positioned to deliver value to both homeowners and commercial clients.
